
The prevention of thoracic outlet syndrome should focus on the design or redesign of the workplace so that workers will avoid carrying heavy weights, reaching overhead, and lifting with the arms above shoulder level. How can we prevent thoracic outlet syndrome? Back to top In some cases surgery may be necessary if symptoms persist for a long time. Physicians may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the pain and inflammation. Avoidance of work activities suspected of causing the condition may be necessary. The initial treatment of patients with thoracic outlet syndrome consists primarily of a carefully planned program of exercise therapy.

How is thoracic outlet syndrome treated? Back to top Special laboratory tests can confirm the diagnosis. The diagnosis is made by medical history and physical examination. How is thoracic outlet syndrome recognized? Back to top

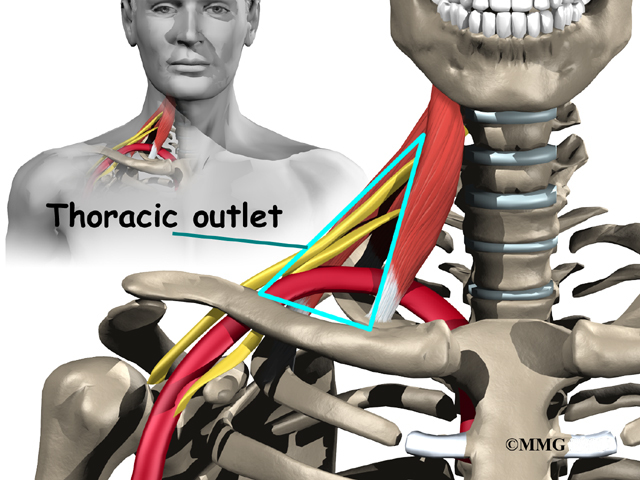
Poor posture - drooping shoulders or holding the head in a forward position.The cause of the compression can vary, but include: What are general causes for thoracic outlet syndrome? Back to top Examples of occupations that are at risk of this syndrome can include dental hygienists, typing on a computer, working on an assembly line, or lifting items above your head. Repetitive injuries from sports related activities can also be a cause of this syndrome. Weak shoulder muscles, long necks and sloped shoulders, poor posture and obesity may contribute to thoracic outlet syndrome. When swollen or inflamed, they can compress the nerves and blood vessels between the neck and shoulders. Work activities involving prolonged restricted postures such as carrying heavy shoulder loads, pulling shoulders back and down, or reaching above shoulder level can cause the inflammation and swelling of tendons and muscles in the shoulders and upper arms. What are the occupational factors of thoracic outlet syndrome? Back to top Nonspecific-type thoracic outlet syndrome - people with this syndrome have chronic pain in the area of the thoracic outlet that worsens with activity, but a specific cause of the pain cannot be determined.Vascular thoracic outlet syndrome - occurs when one or more of the blood vessels (veins or arteries) under the collarbone are compressed.The brachial plexus is a group of nerves that come from the spinal cord and control muscle movements and sensation in the shoulder, arm, and hand. Neurogenic (neurological) thoracic outlet syndrome - occurs when the brachial plexus is compressed.Types of thoracic outlet syndrome include: Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is the general term used to describe a condition caused when the nerves and blood vessels below your neck (between the collarbone and the first rib) are compressed. What is thoracic outlet syndrome? Back to top


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
